
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- Basic Research
- Adipose Tissue and Metabolic Health
- Sung-Min An, Seung-Hee Cho, John C. Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):595-611. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0011
- 4,249 View
- 473 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
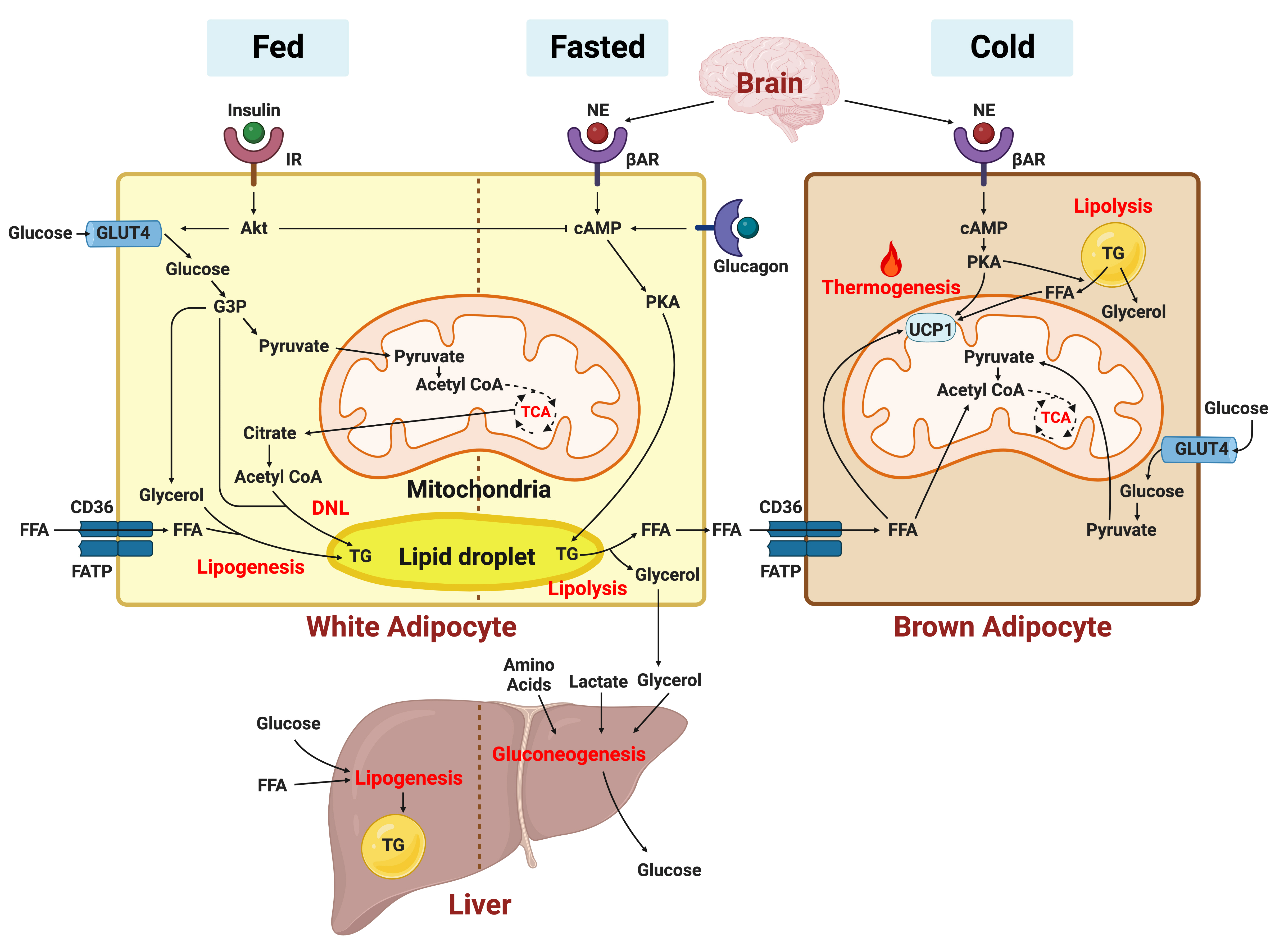
ePub - In this review, we provide a brief synopsis of the connections between adipose tissue and metabolic health and highlight some recent developments in understanding and exploiting adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue plays critical roles in the regulation of systemic glucose and lipid metabolism and secretes bioactive molecules possessing endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine functions. Dysfunctional adipose tissue has a detrimental impact on metabolic health and is intimately involved in key aspects of metabolic diseases such as insulin resistance, lipid overload, inflammation, and organelle stress. Differences in the distribution of fat depots and adipose characteristics relate to divergent degrees of metabolic dysfunction found in metabolically healthy and unhealthy obese individuals. Thermogenic adipocytes increase energy expenditure via mitochondrial uncoupling or adenosine triphosphate-consuming futile substrate cycles, while functioning as a metabolic sink and participating in crosstalk with other metabolic organs. Manipulation of adipose tissue provides a wealth of opportunities to intervene and combat the progression of associated metabolic diseases. We discuss current treatment modalities for obesity including incretin hormone analogs and touch upon emerging strategies with therapeutic potential including exosome-based therapy, pharmacological activation of brown and beige adipocyte thermogenesis, and administration or inhibition of adipocyte-derived factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy–NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads
Srinivasa Reddy Bonam, Dylan Mastrippolito, Philippe Georgel, Sylviane Muller
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2024; 45(1): 81. CrossRef - Senescent adipocytes and type 2 diabetes – current knowledge and perspective concepts
Weronika Kruczkowska, Julia Gałęziewska, Mateusz Kciuk, Adrianna Gielecińska, Elżbieta Płuciennik, Zbigniew Pasieka, Lin-Yong Zhao, Yi-Jin Yu, Damian Kołat, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat
Biomolecular Concepts.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral Adipose Tissue: The Hidden Culprit for Type 2 Diabetes
Sneha Dhokte, Krzysztof Czaja
Nutrients.2024; 16(7): 1015. CrossRef - Beyond the Cold: Activating Brown Adipose Tissue as an Approach to Combat Obesity
Cristina Elena Negroiu, Iulia Tudorașcu, Cristina Maria Bezna, Sanziana Godeanu, Marina Diaconu, Raluca Danoiu, Suzana Danoiu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(7): 1973. CrossRef - Differential Modulation by Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) of Mesenteric Fat and Macrophages and T Cells in Adipose Tissue of Obese fa/fa Zucker Rats
Lena Hong, Peter Zahradka, Carla G. Taylor
Nutrients.2024; 16(9): 1311. CrossRef
- Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy–NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





